BIOS ami detailed instructions. Bios Settings - Detailed instructions in pictures. Standard CMOS Setup
BIOS (Basic Input-Output System) - The basic input / output system, which is stored in the memory of the motherboard and serves to ensure that you and I (in simple words) can control the hardware that is installed on our computer. The BIOS is not the same on all computers and depends on the motherboard.
Incorrect BIOS settings can lead to a decrease in the performance of your computer or even disable it. You can read about your BIOS settings in the passport on your motherboard. But still, I advise you not to especially experiment with the settings, if you are not “on you” with the computer yet.
Issue: Diploma in Ballerinas with honors. Topic: Romance and Germanic languages \u200b\u200band literature. Degree: Honors. Final exam: honors degree from a choreographer. Topic: Dance history, dance art and ballet criticism. Russian, Ukrainian, German, English, French.
For example, to change the order of the drives at boot or to make the drive faster. The manufacturer is also displayed at the very beginning of the download process. This is regulated by the motherboard manufacturer, so only limited features are available for complete systems. The user should not degrade a stably tuned system, if possible. Only rare values \u200b\u200bshould be entered. Until then, changes may be rejected at any time.
After buying a computer, you often need to reinstall the system, because usually installed on them windows versions Vista / 7 Home Basic with a bunch of unnecessary demos or even maybe linux distribution. As you probably already know, there are two of the most common types of BIOS, these are AMI and AWARD. For windows installation you need to change there just one setting and save the results. Let’s do it now.
BIOS troubleshooting
In addition, loading an optimized preset is not the ultimate end to wisdom. However, these line increases are quite risky as a result of equipment damage caused by overheating or an unstable system. On the other hand, most changes need to be done only once - there is no need to rebuild. If you decide, our click show shows how to make your computer faster at no additional cost.
You can assign a Morse code to the table in the manual for the main board. Usually, when you turn on the computer, you hear a short tone that indicates that everything is in order. Of course, only if the internal beeper is connected - unfortunately, unfortunately, this is not always the case.
The simplest, but not always working. Almost all new motherboards or laptops have boot menu (Boot Menu). To get into it, you must press the button when you turn on the computer, most often it is “Esc” or “F12” (sometimes F8 or F11).
Option 1
To boot from a disc, select a CD-ROM to boot from a USB flash drive or other Removable Devices.
To boot from a USB flash drive, you must select USB HDD (USB Memory Stick, etc.)
Often you can find the exact name of the model on the main board. Optimal settings can save valuable system resources. Preferences that don’t know what you are best off changing. In particular, the so-called overclocking of the main memory and the main processor can cause irreparable damage.
A minor building block controls the entire computer. The exact type designation is usually entered on the board. Where is it and how to install it, the step is explained step by step on the next page. The update process is described below. In case of later errors or an unstable computer, you have the opportunity to restore the old values. In an emergency, you can also call the default settings. Restore Defaults Page We show what bios is and how to optimize it.
Option 2
If nothing worked, then again, try looking at the name of the keys at the bottom of the screen at startup, maybe you don’t have this feature at all then use the instructions below.
BIOS setup instructions for booting from a CD or flash drive
You do not need to download or install bios: this is a mini-system software connects to a chip on the main board. It reads the hardware components, and then the operating system boots. BIOS manufacturers describe options on their menus that are slightly different, but very similar. So look for the same names in your version.
It explains the manufacturer’s options separately and provides detailed help. The collection will not develop further. However, he is well informed about the basics of the biosphere and, therefore, remains a valuable source of information. If your BIOS should hit due to incorrect or excessive settings, our action plan will help you in this article.
1.AWARD (PHOENIX) BIOS
How to get into this very BIOS? Turn on the computer and immediately look for “Press DEL to enter Setup” on the monitor. The labels may vary slightly depending on the BIOS version. Presses the DEL button, we get into it, then you need to go to the Advanced BIOS Features section.
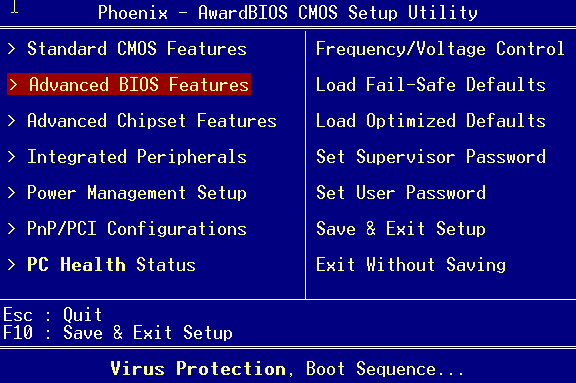
After that, we look in the list of First Boot Device (Floppy or HDD) against it.
Ergonomic optimization: silent fans, low power consumption. But the same is true: if less power is required, the processor automatically reduces the clock speed, thereby reducing current consumption. Lower heat dissipation also has a nice side effect: the fan should rotate less so that the system becomes quieter. Relatively new feature - fan speed control. Depending on the temperature of the case or processor, the fans are dynamically controlled, which reduces noise.
Turn on the speed control function for the connected fans one by one. Rule of thumb: the larger the number, the less consumed. However, the system recovery time takes longer. With the “Auto” option, leave it in the operating system, in what mode it places the computer after a period of inactivity.
2.AWARD (PHOENIX) BIOS
After you turn on the computer or laptop, press the button on the keyboard to boot into the BIOS, most often it is the Del or F2 button. If it doesn’t work, then usually when the computer starts, the access keys are written at the bottom of the screen, you need the one with the word BIOS opposite. If you don’t see anything like this, then try to leaf through the instructions from your motherboard, it is usually applied to the computer.
Pace, pace: advanced settings. Set to Enabled. Disabling unnecessary devices: an increasing number of components on motherboard provides longer system startup times. Requests for a second drive controller or integrated sound card act as a brake. Disconnect controllers and devices that are not needed.
Here you can set unnecessary devices to “Disabled”. Follow step by step: after each change, check how it affects operating system. However, you run the risk of overloading that could result in damage to your equipment.
Different manufacturers motherboards and laptops use a different type of BIOS CMOS Setup Utility, consider the most common options.
Problems registering on the site? CLICK HERE ! Again, the Antivirus Updates section is fully operational - always up-to-date free updates for Dr Web, NOD, Kaspersky all versions. Always the latest versions of the best free programs for everyday use in the section Required programs. There, almost everything that is required for everyday work. Start gradually abandoning pirated versions in favor of more convenient and functional free analogues. If you are still not using our chat, we strongly recommend that you meet him. There you will find many new friends. In addition, this is the fastest and most effective way to contact the project administrators. Do not pass by a very interesting section of our site - visitors' projects. There you will always find the latest news, jokes, weather forecasts (in the ADSL newspaper), a television program for on-air and ADSL-TV channels, the latest and most interesting news from the world of high technologies, the most original and amazing pictures from the Internet, a large archive of magazines in recent years , mouth-watering recipes in pictures, informative. The section is updated daily. Do not have time to read something? The full contents of the creeping line can be found at this link.
We recommend overclocking only in exceptional cases and for advanced users. This is a dynamic overclocking function that is activated only when the processor is fully loaded. This protects all components from too high a temperature. Be especially careful when overclocking.
BIOS fine-tuning
Start at the lowest value. Once the system becomes unstable and crashes, return to the last operating value. For greater stability, optimize the settings for these components. It is even possible that the main board will be provided with new functions that have arisen in the course of technical development. The motherboard manufacturer provides detailed information on how to perform such an update.
BIOS Setup FAQ and BIOS Setup Guide
BIOS Setup FAQ: how to configure BIOS
Introduction
Basic Input Output System BIOS) is recorded in a small flash chip on the motherboard. Most often, this memory is used for reading, but with the help of special utilities and BIOS technologies it is possible to overwrite. During PC startup, the processor on the motherboard executes the BIOS program for the initial check and initialization of the equipment, after which it transfers control to the OS.
Advantage: The software automatically ensures that the file corresponding to the motherboard is downloaded from the Internet. Install and run the tool. Now you can start the installation by clicking the appropriate button. Caution: a power failure or reset during the upgrade process can damage your main board!
If you want to optimize system stability, you must download the default settings for your equipment. To do this, click "Tests" in the main application menu. Record the memory clock. If everything is correct, it will give way to loading the operating system, otherwise it will display an error message or inform us of a failure from the series sound signals or voice, if our motherboard includes this functionality.
If the PC does not go through the boot process, if the system is too slow, Windows crashes, the hardware crashes, then the cause may be an incorrectly configured BIOS. In our article, we will show how, with the help of a competent BIOS Setup, you can solve a particular problem.
The Basics section covers basic BIOS information. In it you will learn what the BIOS is, how to go into the BIOS settings and deal with them. The Key Settings section contains information on the basic BIOS options that every user should be aware of. Experienced users can be advised to immediately go to the "Fine-tune BIOS" section, where you can learn about using hidden settings, activating new functions, bypassing bottlenecks, etc.
In it we get access to the menu in text mode, in which various parameters are classified into categories. The most common are. In this section, we will be able to set the date and time in the system, configure our hard drives and install the drive that we have.
Changing the system time or setting up our floppy drive has no complications. However, the most interesting part is in the “Hard Disk” section, in which the hard disks are configured. The most interesting options. External cache Generally, there is no problem to activate it.
BIOS: Fundamentals and Principles
When the computer starts, the BIOS "presents" the processor to the main components of the motherboard and tells the processor which program to run next, after the BIOS is completed. As a rule, the BIOS transfers control to the boot sector of the drive, which may be a diskette, CD-ROM, DVD or hDD. Boot sector launches a bootloader that activates the main operating system, the same Windows or Linux.
Boot sequence: with this option we will establish the order in which the computer tries to load the operating system from different blocks. In some cases, this option is divided into three different options: the first boot device, the second boot device, and the third boot device.
This section describes the power-saving options for your computer. Power Management: In this section we enable or disable the power-saving feature. To find out which one to use, we will need to read the manual of the device that we are going to connect.
The BIOS is not only responsible for the boot process. Many operating systems use the BIOS as an intermediary to access various hardware.
1. BIOS versions
Each motherboard uses its own BIOS version, specially designed for its hardware. The most common BIOS from Phoenix Award, and in two varieties. In addition, some computers use the American Megatrends BIOS (AMI).
However, despite being lightweight, this is a dangerous process that can leave a plaque unusable if it is not performed properly. This malware, among other things, led to the theft of bank data. The Panamanian pseudonym Dmitry Fedotov and members of the cyber gang were sentenced to five and a half to eight years.
However, this assessment is misleading, as Blackhole has been used as a means of committing a wide range of cybercrimes. In general, the attractive price and depth of the exploits available make the kit attractive to all hackers in the world. Even then, the system manufacturer must provide an appropriate update for the corresponding system.
The BIOS menu structure and designations used vary from one manufacturer to another. Even the BIOS menus for two consecutive motherboard models can vary to some degree. That is why we cannot give an accurate description of the BIOS options of each computer known to mankind. But do not despair. You can easily find a match between the sections below (based on Phoenix Award BIOS) and the BIOS items of your PC. Do not worry if you do not find some settings: this means that the BIOS of your PC does not allow you to manage the specified settings directly.
Therefore, the designation of the chipset is less common. Tomorrow's network will be the eastern, third episode. This brings us back to the main question: but who is this Russian fund that is being implemented in all these online businesses? Then his means. It is difficult to find the details of the distribution of capital in this fund, which invests from one to 200 million dollars. The fund is owned by most of the two founders: Yuri Milner and Gregory Finger. Named in the American Oriental Honorary Roll.
Parameters are classified in these sections as options for which the number of options is generally limited. However, these standard options are also the least beneficial for your configuration. In fact, it is preferable to change one or two parameters, and then start the system, checking whether it works correctly. In fact, it may happen that your computer turns out to be very fast, creating numerous errors that make it unstable. However, using this option is not recommended, as most adapters have their own drivers many times, which may cause interruptions.
2. BIOS output
During boot, when the BIOS checks the hardware components of the system, considers the available memory and finds hard drives and other drives or devices, you can use the special key to enter the BIOS Setup setup program. Often enough to press a key, but other options are used, for example. Carefully look at the screen during boot: in most BIOS it displays a line like "F10 \u003d Setup" closer to the bottom of the monitor. If all else fails, go to the motherboard manual where the magic combination should be indicated. Press the specified key (or combination) and hold for a second or two while booting the PC.
Disable unnecessary options
Waiting cycles. Then it will be changed one way, and then each attempt to annotate the previous value and the new one in order to redo it if a problem arose after the change. These include, for example, emergency mode, emergency mode on the network or the ability to disable forced signature of the driver. So how to return to emergency mode? In the window that appears, you need to click on the “Update and Restore” category, and then “Restore” to find the “Advanced Download” to restart the computer.
If it works, then the BIOS will calculate the amount of available memory, after which the main BIOS menu will appear. If it doesn’t work, then restart your computer and try using a different key combination. For example, many laptops enter the BIOS by pressing the or key. Sometimes keys work, or a combination seems to be.
In the Advanced Download Wizard, you must click "Problem Solving" to use the advanced tools and recovery modes. As a result, you will see an information window in which it is said that everything that can be selected and edited in this mode. When you click “Restart”, the computer will reboot, and the next time the system boots up, the process will automatically stop at the graphically modified old known selection window.
However, this trick can only be used on older or less efficient computers. The only way to get this menu right at startup is the built-in recovery unit. And that's all right: small but smart changes to the default settings often increase the performance of your PC or laptop. We will definitely be in this guide.
3. Change BIOS settings
BIOS setup: use the cursor to select the desired line and press "Enter".
To select a menu in the BIOS, use the cursor and use the arrows to move it to the desired item. Pressing the "Enter" key, you will go to the section or get the settings selection window (as in the illustration below). To change specified setting, you must press the plus keys [+] or minus [-], or another combination like and. From the main BIOS setup menu, you will be taken to various configuration sections, which can be divided into your own subsections.
We open the subsection. The values \u200b\u200bof many options can be changed using the plus keys [+] and minus [-], while others can be set using the drop-down menu.
Let me briefly go through the sections of the main BIOS setup menu.
- In the "Main" or "Standard CMOS Setup" section, you can set the date and time, as well as the parameters of the hard drives.
- The BIOS Features Setup section contains various general settings.
- The Integrated Peripherals section is responsible for interfaces and additional system functions.
- The Power Management Setup section allows you to configure all power and power options.
- In the "PnP / PCI Configurations" section, you can bind interrupts (IRQs) to your PC expansion cards. If such functions are not available in the section, they can be found in the "Advanced" section.
- The "Hardware Monitor" section allows you to find out the values \u200b\u200bof system sensors: processor temperature or fan rotation speed (rpm). Typically, the fan speeds of the processor and the chassis are shown, but also the fan parameters of the power supply unit or others may be present here.
- The "Load Setup Defaults" item restores the BIOS default settings and eliminates any changes you may have made. This item will be useful if your actions led to any problems in the system.
4. Exit BIOS Setup
To complete the BIOS setup, press the key or select the "Save & Exit Setup" main menu item. Sometimes first you need to select the "Exit" item, and then specify the option "Exit & Save Changes". Then the choice is usually offered to save the changes made: "Yes" [Y] or "No" [N]. Select the option you want, after which the computer will restart.
Key BIOS settings
Below we show how to change the boot sequence for bootable disks for a computer in the BIOS, turn on a PC by pressing a button or a “mouse click", activate USB 2.0 support, and also solve problems with fans or hardware configuration changes.
5. Set the boot device priority in the BIOS
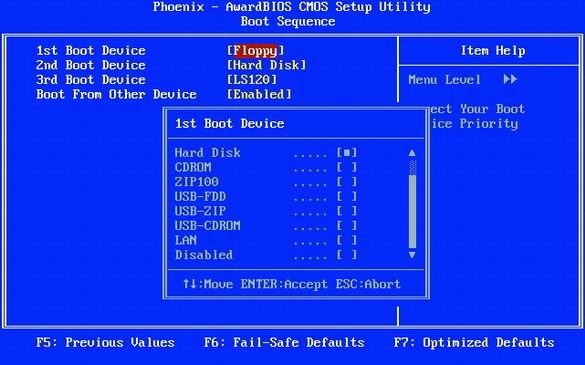
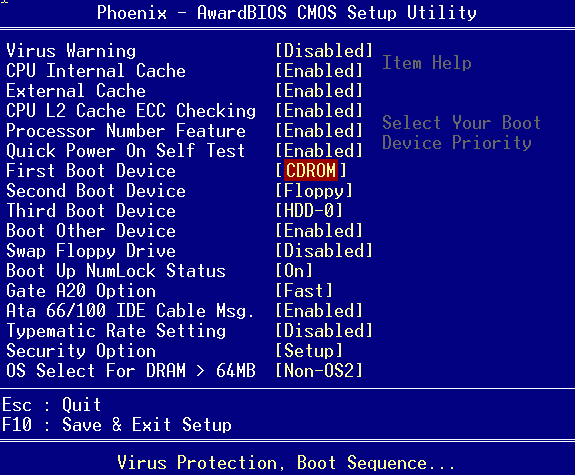
In the BIOS, it is better not to put the drive as the first boot device. Specify a hard drive instead of a drive.
Most PCs set the drive as the priority boot device. This option slows down the PC boot for a couple of seconds, because it will check for a boot diskette in the drive. There is no need to do this because there is a danger of contracting a boot virus from a dirty diskette. And do you often boot from a floppy disk at all? And why do you need this nasty sound of accessing an empty drive? It is better to set the hard drive as the first boot device.
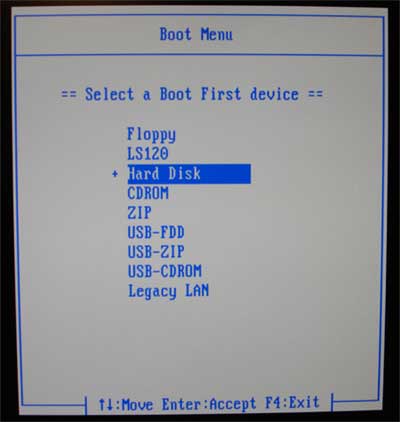
In BIOS Setup, it is possible to specify the devices from which boot is possible, as well as the procedure for checking them. Let's look at how to remove a drive from the first boot device. To do this, select "Advanced BIOS Features, Boot Sequence", then select "1st Boot Device" and change its value from "Floppy" to "Hard Disk", as shown in the illustration above. In principle, a hard disk can be called "HDD-0". As a result, the computer will boot immediately from hard drivebypassing a diskette. Of course, if necessary, the boot order can always be restored by returning to the BIOS Setup.
But now, even if the computer does not try to boot from a floppy disk, it will still check the drive at boot, losing time. To avoid checking the drive, set the "Boot Up Floppy Seek" option to "Disabled".
6. Speeding up PC booting when bIOS help
As you know, to speed up the download, it is important that the PC did not check extra devices, and loaded immediately from the hard drive. In addition, it is better to disable the search for new hard drives and other devices. If you do not often change the set of hard drives in the system, set the search time to zero. To do this, in the "Main" menu, set the "Timeout" to "0".
7. How to enable USB 2.0 support in the BIOS
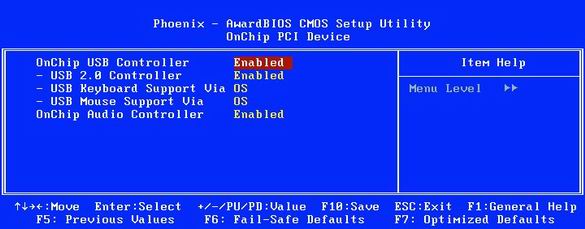
USB: if you installed Windows XP with Service Pack 2, then enable the "USB 2.0 Controller" option.
On many motherboards, the "USB Controllers" option is set to USB 1.1 mode by default. This is due to the fact that Windows XP without Service Pack (and special patches) does not support USB 2.0. That is why USB 2.0 support usually has to be turned on manually.
To enable USB 2.0 in BIOS Setup, set the option to "Enabled" (as shown in the illustration above) or to "V1.1 + V2.0". But remember that to use the USB 2.0 interface, you must install at least Service Pack 1 for Windows XP.
8. How to solve problems with USB devices using BIOS
Some flash drives, MP3 players, and USB sticks are powered by a USB port. If there is insufficient power, the device will not work. That is why you should make sure that uSB port provides enough power for such devices.
Check if your BIOS has an option called "USB 2.0 HS Reference Voltage". If so, set the value from "Low" or "Medium" to "High" or "Maximum".
9. How to change in the BIOS the reaction of a PC to a power outage?
In the "Power Management" section of the BIOS Setup, you can specify how the computer will respond to a power outage. Options "AC Power Loss Restart" or "Restore on AC Power Loss" in the BIOS are responsible for the behavior of the computer after emergency shutdown electricity and subsequent restoration of power. Set this option to "On" or "Enabled" if you want the computer to boot automatically. Either "Off" or "Disabled" otherwise.
10. How to check the temperature and status of the PC through the BIOS
The BIOS provides information about the operating parameters of your PC. You can track in real time the status of vital system components, including CPU, fans, power supply and hard drives. For example, you can turn on the alarm in the BIOS if the processor exceeds a certain temperature, or even implement an emergency shutdown. As a result, your system will not overheat.
Various items in the "Health" or "H / W Control" section allow you to monitor changes in stresses as well as temperature sensors. Most BIOS displays values \u200b\u200bfor the temperature of the processor and the case, and in some versions other temperatures, say, a hard disk or the chipset of the motherboard. In addition, in the BIOS, you can find out the fan rotation speed (in rpm).
11. How to fix problems with coolers using the BIOS
If your PC does not boot, then this may be caused by a too low rotation speed of the cooler or even its stop. Especially often this situation occurs with high-end coolers, whose rotation speed depends on temperature. They can rotate very slowly (or even stop) at a low temperature, as a result of which the BIOS may consider that the fan is out of order. In such cases, the correct BIOS setup helps.
Set the BIOS option "CPU Fan Failure Warning" to "Disabled". When you turn off this option, the computer will boot even if the fan spins at a low speed. Of course, there is another problem: you may not enter the BIOS at all, as the computer may refuse to boot for the reason mentioned above (in many BIOS this option is set to Enabled by default). In this case, you have to temporarily connect any cheap cooler to the motherboard, which always rotates at maximum speed. And after disabling the settings, you can connect the already high-end model.
12. How to avoid a system crash?
Modern hard drives can detect symptoms or problems that precede a drive failure, warning the BIOS about it. This feature is called "Self Monitoring And Reporting Technology" (SMART). Enabling the “HDD SMART Capability” feature allows the BIOS to send alerts to programs like Norton System Works or the widely known free utility SpeedFan. As a result, the user receives information about the state of the drives. This opportunity allows you to take the necessary measures as soon as the first symptoms of the impending failure begin to appear.
13. Connecting old printers and scanners (LPT)
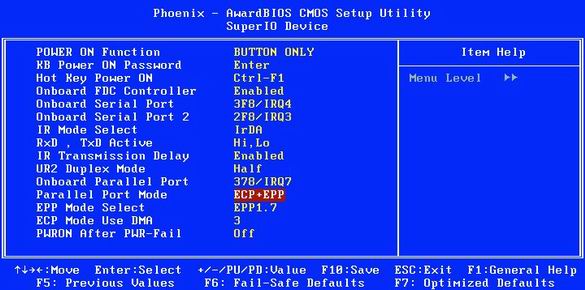
Parallel port: The fastest mode is "ECP + EPP".
Computer Parallel Port (LPT) usually only works in one direction. This setting is suitable for almost all devices, although the transfer rate is limited to 100 kbps. You can put the LPT port in a more modern mode, which gives speeds up to 1 Mbps.
To do this, enable the "ECP" (Extended Capability Port) or "EPP" (Enhanced Parallel Port) mode. In fact, you can enable both modes at once by setting the option "ECP / EPP" or "ECP + EPP".
Warning: if you have several devices connected to the same port, then there may be problems with high-speed modes. In such situations, you can recommend buying a PCI expansion card, which will add a second LPT port. Or buy a USB-LPT adapter. Or, of course, switch to a more modern scanner or printer.
BIOS fine-tuning
This part of the article is addressed to demanding users who want to speed up boot time as much as possible, optimize system parameters, fully utilize the computing resources of the PC, the capabilities of the motherboard chipset and memory.
14. How to enable the BIOS to display the results of the POST test at boot time
During PC startup, many computers display multi-colored logos of manufacturers instead of POST (Power-on Self-Test) lines. But, as it seems to us, it will be much more useful to see which element of the computer is being tested, and with what results.
In the section "Advanced BIOS Features" find the item "Full Screen LOGO Display" and set it to "Disabled". After that, you can observe the results of all PC tests at boot time.
15. How to configure the BIOS so that the PC boots even faster
Using the BIOS, you can further reduce PC boot time, reducing the time of the first test. Of course, we recommend that this be done only if all the components of the PC work stably. Let's say you can enable a single check of available memory in the BIOS instead of three times. To do this, go to the "Advanced" or "Advanced BIOS Features" section, find the option "Quick Power On Self Test" or "Quick Boot" and set it to "Enabled".
Warning: if there are any problems with the hardware, we recommend that you return to the BIOS and turn off the quick test by setting the value "Disabled". In this case, the BIOS is more likely to find an error.
16. How to enable a different graphics card in the BIOS
If your computer has several interfaces into which a graphics card can be installed (integrated graphics, AGP, PCI Express, PCI), then the BIOS will try to determine which one the working card is in when loading. But this is not necessary, because you know all the necessary information!
In the BIOS Setup, select an option called “Init Display First,” which may also be called “Primary VGA BIOS” or “VGA Boot From,” depending on the BIOS version. Specify "AGP" if you are using an AGP graphics card. On new systems with PCI Express, this option is usually called the "PEG Port / Graphic Adapter Priority". In this case, set it to "PEG" if using a PCI Express card.
17. How to disable extra functions of video cards in BIOS
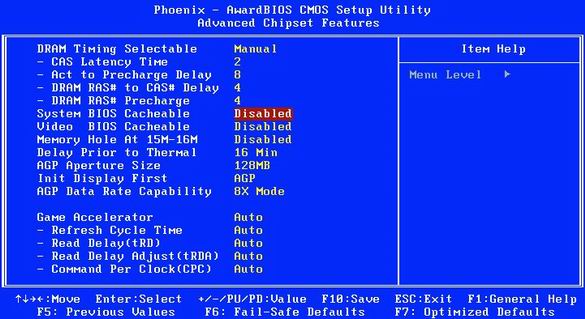
BIOS Cacheable: This option will improve performance only in MS-DOS.
The "Video RAM Cacheable" and "Video BIOS Cacheable" options improve graphics performance on older DOS machines. But for Windows they are useless. There is no need to include them.
Set both “Video RAM Cacheable” and “Video BIOS Cacheable” to “Disabled” in the BIOS. At the same time, disable the option "VGA Palette Snoop", if any. Finally, you can disable the "System BIOS Cacheable" option: it no longer increases performance, and in some cases can even negatively affect system stability.
18. How to properly configure memory for a video card in the BIOS
The option "Graphics Aperture Size" (which may also be called "AGP Aperture Size") was originally intended to make AGP graphics cards more efficiently use the PC's RAM during texture output. This feature is already outdated, as many graphics cards have a built-in memory of 128, 256 or even 512 MB. In addition, the built-in video memory on the card is faster than an operational PC. If earlier it was recommended to set the texture memory value to half the RAM volume of your system, today it is better to choose the optimal size. That is 128 or 64 MB.
19. How to configure the BIOS clock frequency AGP
This "trick" allows you to avoid problems with the AGP graphics card during overclocking of Front Side Bus (FSB).
On motherboards equipped with overclocking, you can find the menu item "AGPCLK / CPUCLK" (it can also be called "AGP Clock"). If it is, then set the value to "Fix". It prevents the effects of FSB overclocking on AGP frequencies. A value of “1/1” causes the AGP to operate at the same frequency as the FSB. A value of “2/3” sets the AGP to 2/3 of the FSB frequency, so, say, a 100 MHz FSB goes to 66 MHz for an AGP graphics card.
20. How to increase the BIOS clock frequency AGP
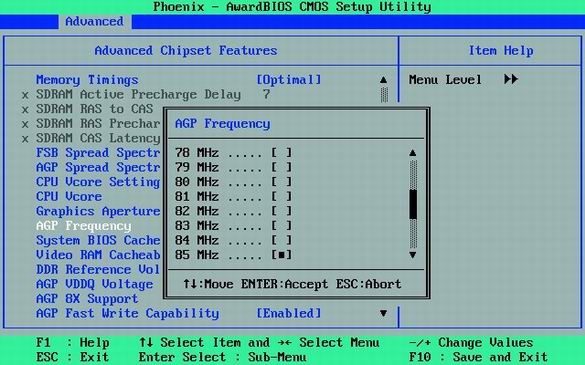
Increasing the AGP frequency increases performance, but it can cause problems.
Some motherboards allow you to increase the frequency of AGP. In principle, you can try to increase this frequency (point "AGP Frequency") in small steps, and reboot the PC after each change. Test each setting on a 3D type shooter Doom 3 or Quake 4 to check system stability. If any malfunctions occur, go back to the previous AGP frequency.
21. How to increase the BIOS voltage on the AGP
Higher clock speeds require more energy. The "AGP Voltage" option allows you to increase the AGP voltage, most often with increments of 0.1 B. The voltage can be increased if an increase in the frequency of AGP leads to instability, and the need for increased productivity is acute.
Warning: in some situations, an excessive increase in voltage can burn the graphics card. If an increase in voltage does not produce the desired effect, return the value to a lower level and lower the AGP frequency to ensure stable operation of the system.
22. How to enable and disable the processor cache in the BIOS
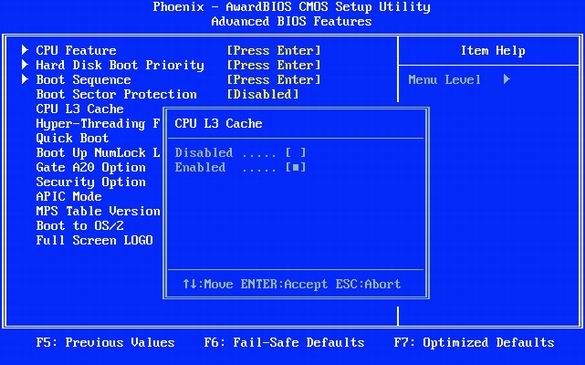
Enabling the processor cache at any level (1, 2, or 3) provides a significant performance boost.
The central processor is significantly faster than other components of the motherboard, and it often has to wait for data to arrive. To speed up the exchange of data allows the processor cache, which is a high-speed memory located between the CPU and the computer's RAM.
The cache of the first level (L1) is very small, but it is located on the processor core, close to the computing units, providing very fast storage for temporary data. The cache of the second level (L2) is significantly larger and can store some elements of the program as a whole or pieces of data. When the processor requests data, it first checks its presence in the cache. If it has the required data, then the performance of the computer increases significantly, because the memory can not respond at the same speed as the cache. Some processors, usually of a professional level, also have L3 cache. As you understand, the cache should always be included.
23. How to enable APIC in BIOS
The motherboard chipset most often consists of two chips, which are called the north and south bridges. They are responsible for transferring data between the processor, RAM, expansion cards and peripherals. Enabling the APIC (advanced programmable interrupt controller) mode in the BIOS allows you to improve the work with devices. The number of interrupts increases from 16 to 24, and managing them with APIC is much easier and more convenient.
All you need to do is go to the "Advanced BIOS Features" menu and set the "APIC Mode" option to "Enabled".
24. How to enable burst mode in the BIOS
Burst Mode allows you to speed up a lot: work with hard drives, PCI cards and RAM. Batch mode allows you to transfer multiple pieces of data in one transmission instead of processing all the pieces individually.
If during the BIOS setup you encounter the “Burst Mode” option somewhere, then set it to “Enabled” mode. Of course, after that we recommend checking the stability of the system.
Warning: many PCI cards may not work properly if the "PCI Dynamic Bursting" option is set to "Enabled".
25. Turn on bus control (Bus Mastering)
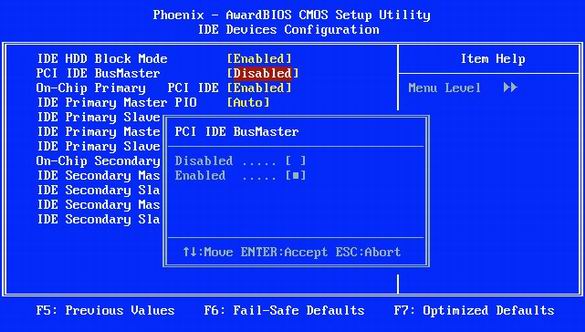
Turn on bus mastering (Bus Mastering): this option speeds up work with the hard drive.
This BIOS setting allows Windows to use the faster Direct Memory Access (DMA) mode when reading or writing to the hard disk. DMA mode provides direct access to the hard disk controller memory, bypassing the CPU. As a result, access to the hard drive is accelerated and precious resources of the central processor are saved.
If the option "PCI IDE BusMaster" is present in the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, set its value to "Enabled", as shown in the illustration above. When you do this, go to Windows in "Start, Settings, Control Panel, System" ("Start, Control Panel, System") and click on the "Device Manager / Device Manager" button on the "Hardware / Hardware" tab. There, find the item "IDE ATA / ATAPI controllers / IDE ATA / ATAPI Controller" (it depends on the chipset, so in your case it may be slightly different). Find the entry “Primary IDE Channel / Primary IDE Channel” and go to the “Advanced Settings” tab. There, find the item "Current Transfer Mode". Its value must be set to "Ultra DMA / Ultra DMA Mode". Hard drives usually have mode 5, and CD / DVD drives have mode 2.
26. How to change memory timings in BIOS
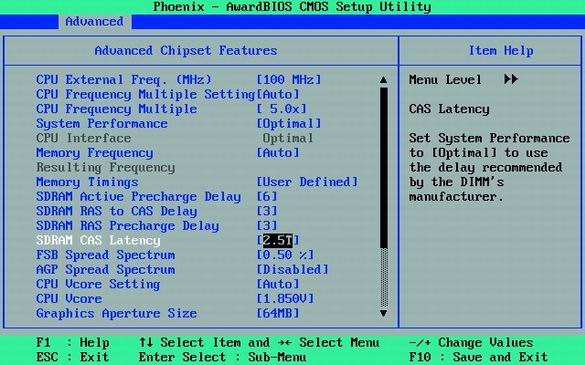
Reduce memory latency. This operation only makes sense for high-quality memory modules. But if it works, then you get a performance boost.
Each SDRAM and DDR / DDR-2 memory module carries a special Serial Presence Detect (SPD) chip, which stores default memory latency (timings). Memory manufacturers usually specify SPD values \u200b\u200bfor guaranteed stable and reliable performance. Therefore, it often makes sense to slightly speed up the delay, since this step allows you to squeeze a few more percent of the performance.
The corresponding options may be called like "System Performance", "Memory Timings" or "Configure DRAM Timing". Typically, the default value for these options is “By SPD”. It forces the computer to read the recommended values \u200b\u200bfrom the SPD chip of the memory module and use them automatically. In addition, the value "Enabled" is also unlikely to cause problems with the PC.
If you want to try to tune the system for better performance, then set the option value to "Disabled" or "User Defined" (if any, see illustration above). Then set the parameters manually as indicated in the following paragraphs.
27. How to reduce RAS-to-CAS latency in BIOS
Memory is best represented as a two-dimensional array. To obtain data, specify the column using the Row Address Strobe (RAS) signal, and then the row using the Column Address Strobe (CAS) signal. Between the RAS and CAS signals, a certain time interval is required so that the addressing does not go astray. Typically, the RAS-to-CAS delay is two or more clock pulses.
The value "SDRAM RAS to CAS Delay" allows you to precisely set how many clock cycles will pass between the RAS and CAS signals. Settings from 2 to 5 are possible, and 2 is the fastest. Try reducing latency and testing the stability of your system. The better your memory modules, the less delay you can get.
28. Reduce the CAS delay in the BIOS
When receiving data from memory, between the setting of the address and the transmission of data, a certain time period should be expected. It is also indicated in measures: 2T for two measures, 3T for three, etc. A lower "SDRAM CAS Latency" value provides better performance.
The correct (and safe) value of "SDRAM CAS Latency" is usually printed on the marking of the module or even burned out on the chips themselves. For cheap modules, 3T or 2.5T are usually found. Set the value to 2.5T or even 2T, and then check the stability of the system. Some memory manufacturers claim that memory supporting 2T mode can work at higher frequencies. If you succeed in reducing the CAS delay, you can try to increase the memory frequency using the "Memory Frequency" option.
Warning: change only one parameter in one test run. Then you can immediately determine the cause of the unstable operation and return to the checked value.
29. Reducing BIOS Precharge Delay BIOS
For memory cells to work quickly, they must be properly charged. The option "SDRAM RAS Precharge Delay" indicates the interval (in steps) between charging the cells and sending the RAS signal. With a lower value, say "2", the memory is faster, but often unstable. Try to reduce the charge delay and check the stability of the system every time.
30. Reduce BIOS SDRAM Precharge
The delay "SDRAM Active Precharge Delay" is also set in beats. It indicates a delay between consecutive accesses to memory, so reducing it may speed up working with memory.
Typically, the delay is calculated as follows: Active Precharge Delay \u003d CAS-Latency + RAS Precharge Delay + 2 (for stability). As in the case of other delays, try lowering its value by one clock cycle and check the stability of the system. If you encounter problems, return the value back.
31. Decreasing memory timings: general tips
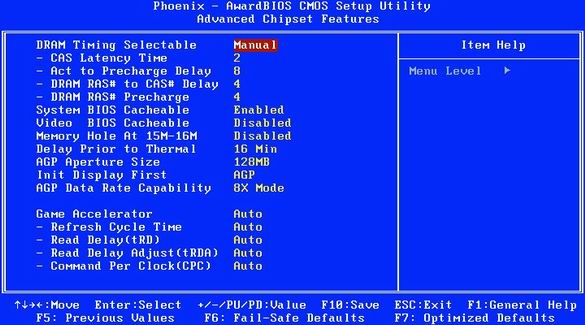
RAM latency: reducing latency can speed up the performance of the memory subsystem.
Recommended values \u200b\u200bfor delays of tips 27-30 depend on the modules themselves. If “2.5-4-4-8” is indicated on the module, then the CAS Latency delay is 2.5 cycles, RAS to CAS Delay - 4 cycles, RAS Precharge Delay - 4 cycles and Active Precharge Delay - 8 cycles. These values \u200b\u200bare recommended by the manufacturer for memory modules. Of course, smaller delays can also work, but at the same time there is a danger of system failures. If you want to get optimal performance, we recommend that you take turns decreasing the latency by one value and testing the system stability every time.
32. Increase memory voltage in BIOS
If memory runs faster, then it will need more energy. That is why, along with an increase in frequency, the supply voltage should also be increased.
The "DDR Reference Voltage" option allows you to increase the memory voltage, usually in 0.1V increments. Increasing the voltage makes sense if you have reduced latency or increased the frequency of the memory. Or if problems began to arise with stable operation.
Warning: too high voltage can burn memory modules!
33. How to turn off the built-in sound in the BIOS
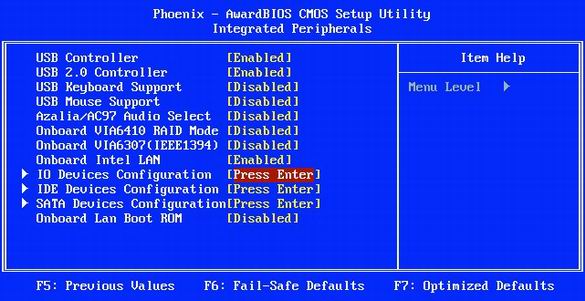
Often, the built-in sound controller of the motherboard is not used. Let's say if you installed a powerful PCI sound card or even use a computer without speakers. Then it makes sense to mute the sound on the motherboard. In some cases, this improves overall system performance and stability.
In the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, set "AC97 Audio Select" to "Disabled" (as shown in the illustration above).
34. How to disable the game port in the BIOS
The game port is useful only to owners of old joysticks or to those users who use it as a MIDI interface. Then it makes sense to allocate two I / O ports and an interrupt to the game port. (By the way, if you have a joystick, then it most likely uses a USB connection). All other users are better off disabling the game port.
In the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, set the value of the "Game Port" to "Disabled".
35. How to disable the network port in the BIOS
Some motherboards have two network interfaces, but as a rule, most users only need one. Disabled interfaces are best turned off. In some cases, this improves system performance and stability.
In the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, set the "Onboard Intel LAN" to "Disabled".
36. How to disable extra ports in BIOS
Today, only older PDAs and modems need serial ports COM1 and COM2. Disabling ports saves two IRQ interrupts, reducing the number of interrupts that the processor should check. Yes, and hardly anybody needs a parallel LPT interface today. Moreover, modern printers and scanners are connected to the USB port.
From the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, disable the COM1 and COM2 interfaces (option "IO Devices, Com-Port", but it may also be called "Serial Port 1/2"). Turn off the LPT port by setting the “Parallel Port” to “Disabled”.
37. How to disable BIOS FireWire (IEEE1394)
The FireWire interface is only needed if you need to download video from a camcorder or connect FireWire peripherals. In all other situations, the interface is better off.
In the "Integrated Peripherals" menu, set the "Onboard 1394 device" to "Disabled".
BIOS update
From time to time, motherboard manufacturers release new BIOS versions. BIOS updates typically contain various optimizations as well as new features. Say the same overclocking features. We recommend updating the BIOS only when the new final version appears (and it is better to skip the beta and alpha versions).
BIOS is written to a special flash memory chip. During the firmware of the new version, it is written to the place of the old one. BIOS updates require special utilities that motherboard manufacturers put in the package. In addition, some BIOS versions support firmware on their own using a key combination.
As for BIOS updates, there are usually two alternatives. You can use the utility for Windows, which can usually be found on a CD from the motherboard or downloaded from the manufacturer’s website. You can also install a utility that will periodically check for a new BIOS version and, if necessary, download it. This method simple, but the verification utility takes up memory space and consumes some resources.
Updating BIOS under Windows is an easy and easy way, provided your system is stable. For greater reliability, you can recommend updating through DOS.
To do this, download the firmware utility from the manufacturer’s website. Then create a bootable DOS diskette and write the utility along with the new BIOS version to it. Then you should boot from the floppy disk and run the utility through the command line (if you downloaded the utility and BIOS in the ZIP archive, you should copy them to the diskette in the unpacked form). Many consider this approach to be more reliable, since there are no extraneous drivers in DOS.
Warning: if you will update the laptop BIOS, you should not do this while using battery power. The laptop should be flashed when powered from the network.
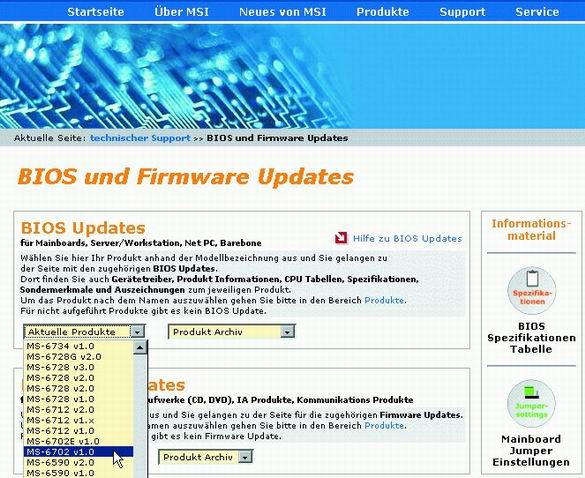
Choose your motherboard: use only those BIOS versions that are specifically designed for your model.
Visit the website of the manufacturer of the motherboard (or computer), and then find the model you need. Most often, motherboard models are called like GA-686BX, A7N8X-E, or K8T Neo2. Sometimes motherboards have two names: retail (say, "K8T-Neo") and technical (for example, "MS-6702 Version 1.0"). The latter is usually indicated on the PCB. When you find a page with your model, click on the "Downloads" or "Support" link.
39. Save old version BIOS
We recommend that you keep the old BIOS version in case the new one is unstable or leads to any problems. You can always flash old BIOS instead of the new version. In addition, we recommend that you carefully read the Readme file, which is present in the BIOS archive. It indicates the changes and additions made to the new version.
40. Think twice before updating the BIOS.
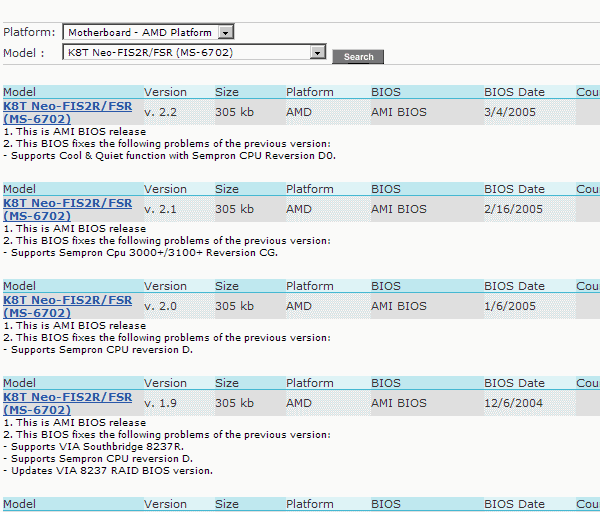
The notes indicated in each BIOS version help you decide whether to update the BIOS or not.
If updating the BIOS solves any specific problem (see illustration above), then you must decide how relevant it is to your system. If the problem does not concern you, then you can skip the BIOS update. Of course, if it does not give any other improvements. Note that a new version The BIOS often allows you to install more modern processors.
If you did not buy the motherboard separately, or immediately bought a branded PC, then in such cases it is better to contact the website of the PC manufacturer. Of course, it is possible that you will find the same BIOS update there as on the motherboard manufacturer's website. However, some PC manufacturers release their own BIOS versions. If you don’t know where to download the BIOS update (from the website of the manufacturer of the motherboard or PC), find out the answer to this question from the manufacturer. If you do not get a clear answer, then updating the BIOS may not be worth it.
41. How to prepare a boot disk with BIOS
When you download the BIOS from the manufacturer’s website, you usually get a ZIP archive containing several files. One of the files contains directly the new BIOS version, and this file is often called very mysteriously: "W7176IMS.110" or "AN8D1007.BIN". In addition, a text document with installation instructions can be found in the archive.
As a rule, the archive also contains the executable file.EXE - a utility for flashing the BIOS. For BIOS Award, it is called "awdflash.exe". In addition, the archive usually contains a batch file that simplifies the firmware process. Most often it is called "start.cmd", "flash.bat" or "autoexec.bat". Unzip these files to any folder. For example, in "C: \\ BIOS \\". If the BIOS archive is self-extracting, then copy it to this folder and run it.
Important: until you start the firmware procedure, print the Readme file, as it may contain important information. Keep the printout with other documentation. By the way, if you haven’t saved the documentation, it can almost always be downloaded from the manufacturer’s website in the form of PDF files.
42. How to write a BIOS to a bootable floppy disk
BIOS firmware requires a DOS boot diskette. To create it, click on the "My Computer / My Computer" icon. Right-click on the drive icon and select "Format ... / Format ...". In the window that appears, check the box "Create boot disk MS-DOS / Create an MS-DOS startup disk ". Then click" Start / Start "to start formatting. Copy the BIOS file and the firmware utility (for example, the files" awdflash.exe "and" w6330vms.360 "for the latest version). Award BIOS).
Then you need to restart your computer and boot from a floppy disk. To do this, make sure that the drive in the BIOS is set as the first boot device. After rebooting, enter the BIOS setup menu by pressing the appropriate key. Select "Advanced BIOS Features, Boot Sequence", which may also be called "Advanced, Advanced BIOS Features" on some PCs. Ensure that the 1st Boot Device option is set to Floppy. Go to the main BIOS setup menu by pressing the key, then use the key to exit the BIOS setup menu. If you want to save your changes, then press the [Y] ("Yes") key.
43. How to flash BIOS under DOS
Ensure that the computer is receiving stable power. As we mentioned earlier, do not flash the BIOS on a laptop if it is running on battery power. Plug the laptop into a power outlet.
Boot the PC from the diskette on which you wrote the firmware utility and the BIOS file. AT command line enter the name of the firmware utility, and after a space - the name of the file with the BIOS. In our example for the Award BIOS, it will be a line of the form:
A: \\\u003e awdflash.exe w6330vms.360
The firmware utility starts, which guides you through all the other processes.
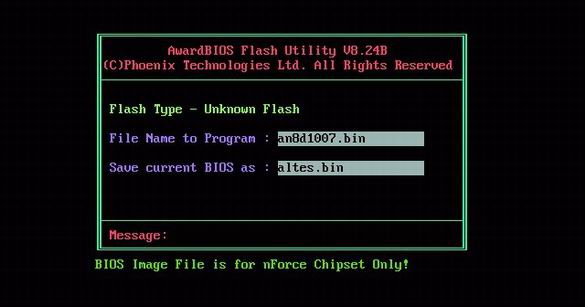
Keep the old BIOS. Before flashing a new BIOS version, we recommend that you keep the old version by entering a file name.
Although the name of the firmware utility and the BIOS file may differ in your case (for example, "awdfl789.exe" and "w6330vms.250"), the approach does not change. Follow the utility instructions and answer correctly. During each BIOS update, keep the old version just in case. It will allow you to go back if there are any problems in the new BIOS version.
Finally, the firmware utility will overwrite the BIOS image in flash memory to the new version. After successful completion, restart the PC. During the firmware, you need to make sure that the computer does not have power turned off. Otherwise, you will have to contact the service center (or craftsmen) and flash the BIOS through the programmer.
44. Configuring the new BIOS
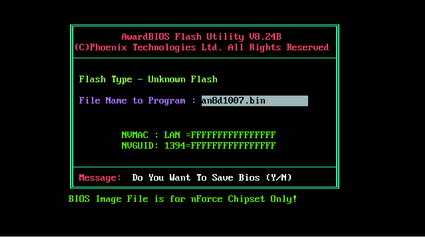
When the BIOS update is completed, restart the computer, preferably in a "cold" way (by turning the power off and on). In some cases, a CMOS reset may be required (see below). After switching on, the lines will be displayed. bIOS bootwhere the new version should appear. Enter BIOS setup using the necessary keys. Select the option "Load Optimized Defaults" (it may be called "Exit, Load Setup Defaults" on some PCs), which will load the default settings. Make any necessary changes to the BIOS settings. Exit the setting with the key, then press [Y] to save the setting. Then enjoy the products of your labor!
Golden BIOS firmware rules
In principle, by changing the BIOS settings, you can hardly do irreparable harm to your computer, unless you overstate the power supply too much. In any case, it’s better to remember a few golden rules.
- Create backup current version BIOS Before flashing a new BIOS version, keep the old one. In each BIOS firmware utility, it is possible to save the old version, for example, "Save current BIOS as". If the new version is problematic, you can always return to the old one.
- Change only one setting at a time. If you went into BIOS setup, then make the changes carefully, one at a time and in small steps, if possible. After each process, restart your computer and conduct testing under Windows to identify any instabilities. This is the only way to determine how a particular setting will affect the performance and stability of your PC.
- Use stress tests. To check the stability of the PC, it is best to load the computer to the maximum. You can run games, video editing applications, 3D tests like 3DMark 2005, etc.
- If all else fails, try a cold boot. If the computer refuses to boot after pressing the reset key, then turn off the computer from the network and wait a couple of minutes. Use the power cable disconnect or toggle switch on the power supply, rather than the shutdown keys on the front of the PC.
- Reset CMOS. If the PC refuses to boot after changes made to the BIOS, then you cannot return the settings back. In such cases, resetting the CMOS helps. Follow the CMOS reset instructions for your motherboard. In some cases, to reset the CMOS, you must close (or open) the jumper by sending a "Clear CMOS" signal. Or you need to use the DIP switch. Do not forget that after resetting the CMOS you need to return the jumper to its original position. Alternatively, you can get the battery of the motherboard and disconnect the computer from the network. But at the same time, sometimes you need to wait a few hours.
BIOS Setup: Manual
Introduction to BIOS Setup
The Basic Input-Output System (BIOS) is an important part of the procedures of any PC, which is stored in a separate chip on the motherboard. At its core, the BIOS is an intermediary between the computer hardware and the operating system. Without BIOS, the operating system could not communicate with and manage the hardware.
In other words, the BIOS is an essential component of any computer. If the BIOS settings are set incorrectly, then the performance of your PC can be reduced up to 40%. Unfortunately, as new processors and motherboards become available, BIOS options continue to become more and more confusing. As a result, many users simply do not understand the meaning of many options of modern BIOS.
But don't despair - THG comes to the rescue! Each motherboard and / or computer uses a different BIOS, so we will consider an example of BIOS optimization based on the Asus A7N8X-E Deluxe motherboard. We chose this motherboard, because after it came a large number of other ASUS motherboards with similar BIOS. In addition, the A7N8X-E is one of the most popular ASUS models: it has been on the market for almost two years and is still sold for AMD systems. It is likely that your motherboard will have some differences from this model, but then you can get an idea of \u200b\u200bthe possible adjustments.
Remember that incorrect BIOS settings can lead to unstable PC operation. In this case, you will have to reset the BIOS to the factory default value (that is, to non-optimized ones). This is usually done using a jumper on the motherboard, but how to reset the BIOS on a laptop? None of the parameters discussed here should adversely affect the operation of your PC, but be sure to follow each step.
Many major computer manufacturers, such as Dell, HP, Gateway, and Micron, limit the options available in the BIOS to reduce the number of calls to support due to improper configuration. Therefore, for computers from some manufacturers, you will not be able to enable certain advanced options mentioned in our article.
During boot, most PCs briefly display a message about how you can go into the BIOS setup. You will have a few seconds to press the required key - if you do not have time, the operating system will start to load. To enter the BIOS after turning on the PC, hold or continuously press the desired key. On most PCs, it is “DEL,” “F1,” or “F2.” If your PC does not enter the BIOS setup using these keys or does not display a message on how to do this, you will have to refer to the documentation or support service of the manufacturer of your PC.
We recommend that you restart your computer after changing each BIOS option to ensure that the system is stable. Think for yourself: if you make several changes to the options in the BIOS and your system stops loading, how will you look for the cause of the error?
Let's start with the menu of the main BIOS options (Main Options), which can be called up by clicking on the "Main" tab in the upper left corner.
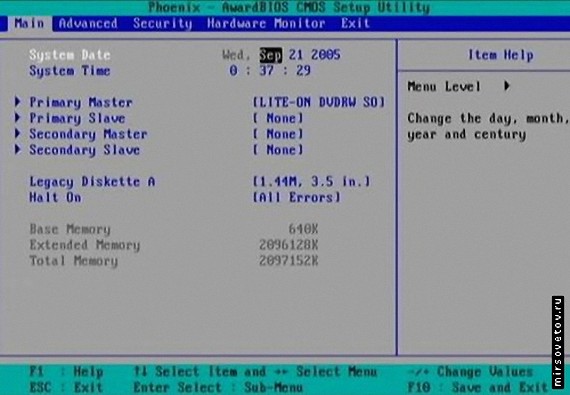
Below you can set the time and date, as well as the parameters of your hard drives and other installed drives. Each time you boot the PC, most likely it automatically detects the drives installed in the system. Most computers take a second or two to do this, but if you manually enter the necessary parameters, speed up the boot time somewhat.
To do this, select the drive by moving the cursor to it and press "Enter". Then write down the value for Cylinders, Heads, Sectors, and LBA. Some BIOSes have options for block mode ("Block Mode") and for 32-bit transfer mode ("32-Bit Transfer Mode"). Change the drive type from "AUTO" to "USER". Then enter the same numbers that were displayed. On most modern computers, you should turn on the “LBA Mode,” “Block Mode,” and “32-bit Transfer Mode,” even if they have been turned off before.
If none of the drives are connected to this controller channel, select NONE. For example, if your hard drive is configured as primary on the first channel (Primary Master), and the CD-RW drive is configured as primary on the second channel (Secondary Master), make sure that the secondary drives (Primary / Secondary Slave) on each channel are set to NONE If you leave the AUTO option without a device, the computer will each time check for the presence of a drive. Setting the value to NONE where there are no drives will speed up the download a little.
Then select the “Advanced” tab, which will be divided into several submenus. The first branch is called "Advanced BIOS Features."
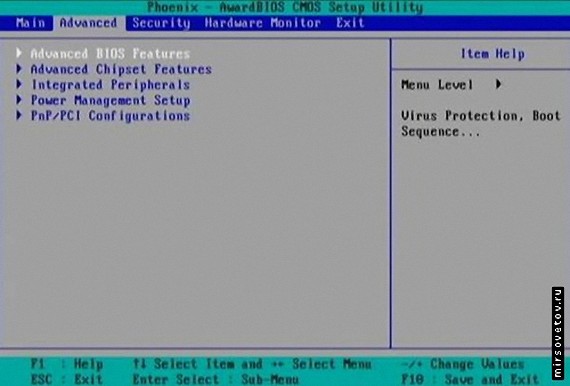
Do you need to thoroughly test your memory and drive every time you turn on your computer? Unless you suspect there is a problem with one of these components, it hardly makes sense to run BIOS diagnostics every time. In this part of the BIOS, you can reduce the system startup time by enabling or disabling certain functions. For example, those that we indicated above. Below are recommended settings.
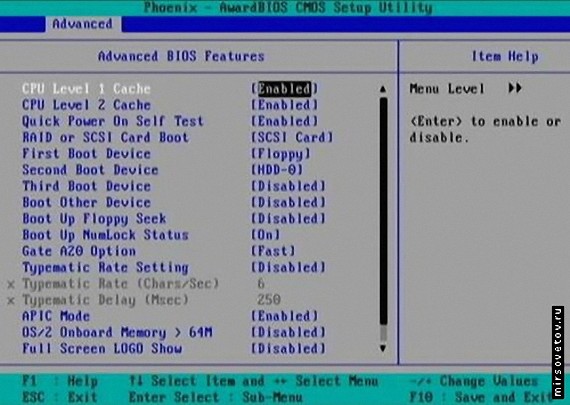
Boot virus detection (definition of boot viruses): "Enabled" (enabled). Sometimes this item is located in the main BIOS section ("Standard" or "Main"). Today, boot viruses are not as common as before, but this feature will protect your data when booting from an infected floppy disk or CD-ROM.
CPU Level 1 Cache (processor L1 cache): "Enabled" (enabled).
CPU Level 2 Cache (processor L2 cache): "Enabled" (enabled).
Quick Power On Self Test (quick test): "Enabled" (enabled). This item allows you to avoid repeated memory testing several times when you turn on the PC. If you have bad memory, then this test still will not determine it.
First, Second, or Third Boot Device (first, second or third boot devices): set the boot order and disconnect all devices from which you do not plan to boot.
Boot Other Device (booting from another device): "Disabled" (disabled), unless you plan to boot from a network card or SCSI device.
Boot Up Floppy Seek (check drive at boot): "Disabled" (disabled). Extra waste of time, and extra noise.
Boot Up NumLock Status (state of the "NumLock key" on boot): choose yourself here. Some people like that the NumLock key is activated when Windows starts, others don't.
Gate A20 Option (Option Gate A20): FAST (fast). Although this feature has already lost its meaning under Windows XP, we still recommend leaving it enabled. Older versions of Windows and OS / 2 work better if the parameter is set to FAST. The only reason this parameter is set to "Normal" is to load DOS.
Typematic rate setting (dialing speed): "Disabled" (disabled). Choose yourself here. This parameter determines how often keyboard characters will be pressed if you hold down a particular key.
APIC Mode (APIC mode): “Enabled”. Behind APIC lies the Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller, which is responsible for supporting multiple processors, additional IRQs, and faster interrupt handling.
OS / 2 Onboard Memory\u003e 64M (OS / 2 memory\u003e 64 MB): "Disabled" (disabled). This setting applies only to users who will run the now obsolete OS / 2 operating system from IBM.
Full Screen LOGO Show (full screen logo display): your choice. When this option is enabled, the memory counter and Power-On Self-Test (POST) are hidden behind the graphic picture. If this option is disabled, then you see a normal loading screen. Actually, it is present on most computers. Some users like to hide the POST screen, while others like to watch the process.
POST Complete Report (full POST report): choose for yourself. When you enable this option, you will receive a full POST report.
Overclockers and enthusiasts trying to increase system performance often increase the frequencies of the bus and processor core. In addition, they often increase the voltage of the components, since it is possible to achieve higher clock frequencies, however, more heat is released.
Overclocking no longer leads to the same performance difference that we got used to a few years ago. In addition, overclocking deprives the user of a guarantee, can lead to failure of components, and the system can work unstably. For this reason, for most frequency and voltage settings, the "AUTO" option should be left in this BIOS section. If you want to adjust the settings, then click on the "Advanced" tab bIOS screen, then select the "Advanced Chipset Features" branch.
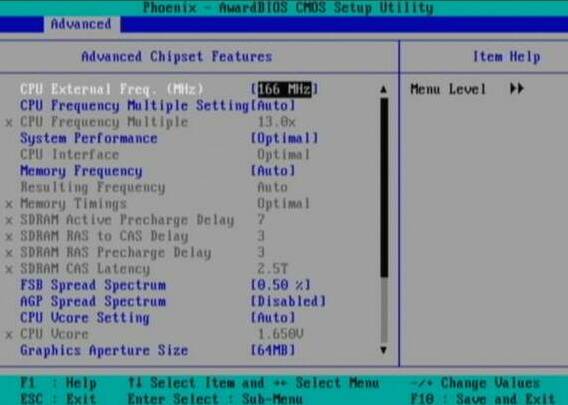
CPU External Freq. (MHz) (external processor frequency, MHz): make sure that it is set in accordance with the specifications of your processor.
CPU Frequency Multiple Setting (setting the processor multiplier): AUTO.
CPU Frequency Multiple (processor multiplier): Make sure that the multiplier is set according to the specifications of the processor.
In other BIOSs, the multiplier item may be called "CPU Multiplier". To understand the value of the multiplier, remember that the frequency of the processor is different from the rest of the components of your system. In our example, we use the AMD Athlon 2600+ processor, whose frequency is 2133 MHz. The FSB processor bus frequency is 133.33 MHz. The processor frequency of 2133 MHz (2.133 GHz) is set by multiplying the FSB frequency by a factor. In this case, we just get 16 x 133.33 \u003d 2133.
Through testing, AMD determined that the 2133-MHz processor is as fast (or even faster) as the Intel processor frequency 2.6 GHz Since consumers typically use a clock speed to measure performance, AMD had to find a way to convince customers that a lower clock speed aMD processors does not mean less performance. For this, model numbers were introduced. Therefore, do not be surprised that the AMD Athlon 2600+ (in our example) actually works at 2.133 GHz, and not at 2.6 GHz.
System performance (system performance): "Optimal" (optimal).
CPU Interface (CPU interface): "Optimal" (optimal).
Memory frequency (memory interface): "By SPD" (via SPD). Most memory module manufacturers add a special chip (Serial Presence Detect, SPD) that reports Computer BIOS module size, frequency, voltage and other memory parameters. These settings are determined by the manufacturer to ensure maximum performance and reliability. That is why we recommend leaving the option "By SPD". If you adjust the memory settings manually, you can squeeze out a little more performance. But be careful: in this case, the system may begin to "fly off" at random times, not boot properly, or refuse to boot at all.
Overclocking Options in Advanced BIOS Settings, Continued
Memory timings (memory latency): "Optimal" (optimal).
FSB Spread Spectrum: "Disabled" (disabled). This feature allows systems to pass the European Electromagnetic Interference Test (EMI). It is constantly changing, albeit slightly, the frequency of the Front Side Bus (FSB). It should be remembered that the inclusion of this function can affect the interruption of the Internet connection, as well as cause stability problems during system overclocking.
AGP Spread Spectrum: "Disabled" (disabled). The same is true here as indicated in the previous paragraph. Except that the frequency of the Advanced Graphics Port (AGP) interface is modulated.
CPU VCore Setting (setting the voltage of the processor core): "AUTO".
CPU VCore (processor core voltage): Make sure that this setting is set to the specifications of the processor.
There are so many different processors on the market today that hardly one example can describe them. Below we have given a partial table showing the name of the CPU, the actual operating frequency, the nominal core voltage and the maximum allowable temperature.
| Athlon processors | Frequency (GHz) | Core Voltage (V) | Max. temperature (° C) |
| XP 1700 | 1,467 | 1,50 | 90 |
| XP 1900 | 1,60 | 1,50 | 90 |
| XP 2000 | 1,667 | 1,60 | 90 |
| XP 2100 | 1,733 | 1,60 | 90 |
| XP 2200 | 1,80 | 1,60 | 90 |
| XP 2400 | 2,0 | 1,60 | 85 |
| XP 2600 | 2,133 | 1,65 | 85 |
| XP 2700 | 2,171 | 1,65 | 85 |
| XP 2800 | 2,250 | 1,65 | 85 |
Graphics Aperture Size (AGP aperture size): 64 MB or 128MB. This function controls the Graphics Address Relocation Table (GART) and the amount of memory that the AGP bus can address. Regardless of the memory size of your graphics card, we recommend specifying 64 or 128 MB. As a result, the video card will provide optimized performance, even if the application requires additional memory for textures - at the same time, GART will not go beyond reasonable limits.
AGP Frequency (AGP frequency): "AUTO".
System BIOS Cacheable (system BIOS caching): "Disabled" (disabled). You might think caching is good. Yes, but not always. Enabling this function can lead to a system crash if the program tries to write data to the cached area of \u200b\u200bthe BIOS. If you use DOS, then it’s better to enable the function.
Video RAM Cacheable (video caching): "Disabled" (off). This option allows you to copy the video memory directly to the L2 cache, which is faster than the ROM of the video card. However, Windows today has moved much further than DOS, so the graphics card ROM is used very rarely. Since the L2 cache is limited in size, we recommend using it to increase the efficiency of other tasks.
DDR Reference Voltage (voltage of DDR modules): 2.6V. The setting is responsible for the voltage of the Double Data Rate (DDR) memory modules of your system.
AGP VDDQ Voltage (AGP VDDQ voltage): 1.5V. VDDQ is a technical abbreviation (Voltage between Drain and common for Data Quad-band). But we will not go into details. You just need to understand that the voltage of the AGP port of the video card is set here.
AGP 8X Support (AGP 8X support): enable this option if your video card supports 8X AGP interface. In addition, VIA 4-in-1 drivers should be installed on motherboards with a VIA chipset.
AGP Fast Write Capability (support for fast recording AGP): we recommend enabling this option. This feature allows you to bypass the main RAM when recording from the chipset to the AGP device, increasing productivity up to 10%. However, some cards and games may have problems turning this feature on. We recommend experimenting to determine which setting is best for your PC.
This BIOS section contains settings for the embedded peripherals installed on the motherboard. This includes serial and parallel ports, audio, LAN, USB ports, etc. If some ports are not used, but they are enabled in the BIOS, then the ports consume extra system resources. They are still better off.
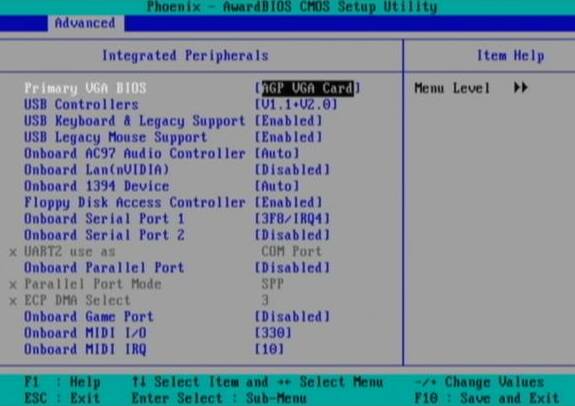
Primary VGA BIOS (main BIOS VGA): this function is used only if two graphics cards are installed in your PC: one AGP (accelerated graphics port) and one PCI (peripheral component interconnect). The system must know which card to initialize first and consider the main one. If you have one video card, then most likely it supports the AGP interface. For most cases, the default setting is incorrect and should be changed to AGP VGA Card. If you really have two video cards, then choose the main one from them. It will display information from the POST test and OS boot.
USB controllers (USB controllers): This function limits the functionality of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) controllers on your PC. You can select "USB 1.1 only", "USB 1.1 and 2.0" and turn off USB altogether. For most users, the best option would be to configure USB 1.1 and 2.0
.USB Legacy Support (support for hereditary uSB devices): this function should be enabled if your PC is equipped with a USB keyboard and you want to use it in a DOS environment or before loading the OS (in the boot menu, for example). If the setting is turned off, the keyboard will not work after booting from a floppy disk or CD-ROM. And you can’t enter the BIOS either. If your PC uses a USB keyboard (rectangular connector), set the setting to "Enabled". If you have a PS / 2 keyboard (round connector in cross section), set "Disabled". Please be aware that turning this feature on may cause wake up problems from Standby or Hibernate modes, or cause the PC to shut down incorrectly. In other words, activate the function only if necessary.
USB mouse support (USB mouse support): the same is true as for the previous paragraph. It is best to disable this option.
Onboard AC97 Audio Controller (built-in sound controller AC97): if your PC is equipped with an additional sound card, for example Sound Blaster Audigy, or your system does not have speakers, then disable the built-in sound card ("Disabled"). Then you free up precious resources and prevent potential conflicts. However, many computers use integrated sound solutions, so there you should leave the option turned on ( "Enabled").
Onboard AC97 Modem Controller (built-in AC97 modem controller): Some motherboards use a built-in modem for dial-up access. If there is no modem socket, the modem is not needed at all, or a separate modem card is used, then the option should be disabled ("Disabled"). Otherwise, enable ("Enabled").
Onboard LAN (nVidia) (built-in LAN controller): this option enables or disables the built-in network card. The options are "Auto" or "Disabled" (disabled). The ASUS motherboard used for our review has two built-in network cards, which are especially useful when a PC is used as a router to distribute an Internet connection: one lAN card connects to the cable / DSL modem, and the second to the switch of your network. If you use only one network port or you do not need a network at all, then turn off the controller to free up valuable resources.
Onboard LAN (3Com) (built-in LAN controller): this option applies to the second built-in LAN controller. The same thing is true here, as stated above.
Peripheral Settings in BIOS (Integrated Peripherals), continued
Onboard 1394 Device (FireWire) (1394 Embedded Controller): This function enables or disables the built-in IEEE 1394 (FireWire) port of your PC. If you are not using any FireWire devices, then turn off the option to free up valuable resources.
Floppy disk access controller (drive controller): Most modern boards do not have drives. If this is true for your PC, or you do not need a drive, then unplug it and free up resources. Note: if you have a drive installed and you turn it off in the BIOS, you cannot work with it until you turn it on in the BIOS again.
Onboard Serial Port 1 (built-in serial port): most users no longer use serial ports to connect peripherals, because today this interface has almost completely replaced USB. If you are not using serial ports, then disable them to free up resources. On the other hand, if the serial port is used, then set the option "3F8 / IRQ4".
Onboard serial port 2 (built-in serial port): the same is true as above. If the port is in use, set the value to "2F8 / IRQ3".
UART2 Use As (usage type UART2): UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver / Transmitter) is a chip that receives and transmits data sequentially. Each serial port uses this chip, although it is possible to integrate multiple UARTs into one chip. Many motherboards offer contacts for connecting an infrared port instead of COM2, so choose it yourself. But remember that for the infrared port you should install the IR adapter, usually sold separately.
Onboard parallel port (built-in parallel port): this function allows you to select the parallel port mode or disable it altogether. If you do not use a parallel port, then disabling the option will free up valuable system resources. If the port is used, we recommend setting the value "378 / IRQ7".
Parallel port mode (parallel port mode): if you disabled the parallel port, then this setting does not matter. However, when you enable the parallel port, you can set the modes to "EPP" (enhanced parallel port) or "ECP" (enhanced capabilities port). EPP mode is recommended if your system is equipped with only one device using a parallel port (for example, a printer). Select "ECP" if several devices are connected to the port: say, an external zip drive, scanner, printer, or tape drive. Make sure you use IEEE 1284 certified parallel cables.
ECP DMA Select (selection of the ECP DMA channel): if you select the “ECP” or “EPP plus ECP” modes for the parallel port, this option will also appear. With it, you can set the channel direct access to memory (DMA, Direct Memory Access), which you plan to use. We recommend the default value of "3".
Onboard game port (built-in game port): if your system has a separate sound card, or you are not using MIDI devices or old joysticks, then this function should be turned off in order to free up valuable resources. If you use the built-in game port, then set the default value to "201".
Onboard MIDI I / O (built-in MIDI interface): MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) allows you to associate musical instruments with the hardware and software components of a PC. If the computer is not used to connect external MIDI devices, feel free to disable the option. Otherwise, we recommend the default value of "330".
Onboard MIDI IRQ: same as above. If you use MIDI devices, then set the default setting to "10".
Most users are confused in this area of \u200b\u200bBIOS. If the correct settings are not set here, the system will stop turning off properly, and will also not exit the Standby or Hibernate states correctly. Since Windows already has built-in power management, you can turn off all relevant options in the BIOS. Otherwise, they will conflict with each other, and none will work correctly. Motherboard manufacturers understand that not everyone uses Windows, so most settings are intended for users of other operating systems.
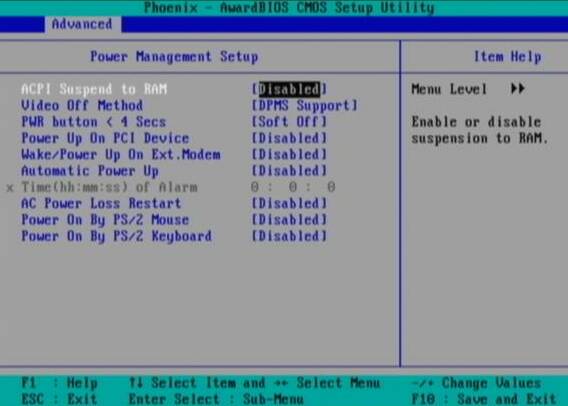
ACPI Suspend to RAM: ACPI stands for “Advanced Configuration and Power Interface” - do not confuse it with APIC or IPCA, which are also present as options in some BIOSes. The Suspend to RAM function, also called S3 / STR, allows the computer to save more power in standby mode, but all devices connected to the computer must be ACPI compatible. Some BIOSes have the option "S1 / POS" for this scenario. If you enable this function and you have problems with the standby mode, then go back to the BIOS and turn it off.
Video Off Method (way to turn off the video): DPMS stands for "Display Power Management System". This option allows the BIOS to control a graphics card that supports the DPMS function. The “Black Screen” option simply produces a blank black screen - it should be used for monitors that do not support the “green” options or the power saving mode. Option "V / H SYNC Blank" not only gives a black screen, but also turns off vertical and horizontal scanning. If your computer and monitor have been released in the last five years, then we recommend the "DPMS" option.
HDD Down In Suspend (HDD shutdown in Suspend mode): the function determines whether the hard disk will automatically turn off in Suspend mode. Most of these settings are managed by Windows, but if your hard drive does not turn off when the computer enters "Suspend" sleep mode, then enable this option. Otherwise, it is better to leave it off ("Disabled").
PWR Button< 4 Secs (power key): By default, all ATX computers turn off if you hold the power key for more than four seconds. This setting tells the computer what to do if the power key is held for less than four seconds. You can either turn off the system or put it in Suspend mode. So decide for yourself.
Power Up On PCI Device (enable via PCI device): if you use Wake-On-LAN - this option is often used in large office environments to remotely turn on computers - then leave this option enabled ("Enabled"). Otherwise, we recommend disabling this option ("Disabled").
Wake / Power Up on Ext. Modem (activation via external modem): this function allows the computer to automatically turn on when the modem telephone line is activated. Again, a convenient feature for remote control. In other environments, that is, for most users, it is better to turn it off ("Disabled").
Automatic power up (Auto Power On): This function allows you to set the time when your computer will automatically turn on. If you need a similar function, then enable it ("Enabled"). Otherwise, turn off ("Disabled").
Time (hh: mm: ss) of Alarm (turn-on time): the time for automatic turn-on is set here. Remember to enable the "Automatic Power Up" feature.
AC Power Loss Restart (power on after loss of power): this option tells the computer what to do after an unexpected loss of power and its recovery. If the option is disabled ("Disabled"), then the system will not start. If enabled ("Enabled") - then the system will reboot. We recommend disabling this option ("Disabled").
Power On By PS / 2 Mouse (enable via PS / 2 mouse): if this option is enabled, a PS / 2 mouse (not USB) can be used to turn on the PC. Disable ("Disabled") this option to not turn on the computer by accidentally touching the mouse.
Power On By PS / 2 Keyboard (switching on via PS / 2 keyboard): when this function is activated using the special keys, you can turn on the system. It is better to turn off the function ("Disabled") so as not to accidentally make a mistake with the key.
This area of \u200b\u200bBIOS exists mainly to solve compatibility problems with old hardware. Most users do not need to change the default settings here.
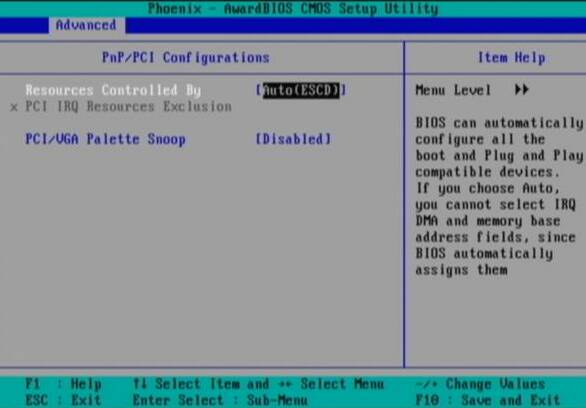
Reset configuration data (reset configuration data): ESCD (Extended System Configuration Data) data contains information about all non-PnP devices (plug and play). It also stores information about the system since the previous boot. Enable this option to clear data during the Power-On-Self-Test (POST). Typically, cleaning is done when diagnosing a component that does not work properly. After enabling the option ("Enabled") and exiting the BIOS, the configuration data will be cleared, and the option will automatically turn off ("Disabled").
Resources Controlled By (resource management): this setting allows the computer to either set the IRQ automatically, or assign all devices IRQ manually. Remember that manually specifying an IRQ can cause problems. This option is only necessary when working with old, non-PnP peripherals. We recommend setting “AUTO” (ESCD).
IRQ Resources (IRQ resources): this option will allow you to manually configure IRQ. It is activated only if in the previous paragraph you selected manual indication ("MANUAL").
PCI / VGA Palette Snoop: This function usually refers to additional graphics cards like MPEG encoders. They do not have their own color palette, so they should receive (snoop) the palette from the system video card. If, like most users, you do not have an additional video device connected to the video card, then disable this setting ("Disabled").
BIOS security options allow you to restrict third-party access to the BIOS or computer so that they do not make any changes. Since BIOS settings are critical for the proper operation of a PC, many company administrators block the BIOS with a password.
Security option (security option): this option allows you to protect BIOS changes with a password ("Setup" option). In addition, you can specify here that the password is requested each time the PC boots up (option "System").
Set supervisor password (set administrative password): if you specify an administrative password, it will be requested when entering the BIOS (if the "Setup" option is selected above). If in the paragraph above you specified the option "System", then a password is required for a cold boot.
Set user password (set user password): here you can specify the password that will be requested from users when loading the PC. If Supervisor Password is also specified, then in the BIOS the user can only change the time and date.
Note: if you forget or lose passwords, you will have to reset the BIOS to factory settings by temporarily changing the jumper on the motherboard.
In this part of the BIOS, you can track voltages, fan speeds, and temperatures. On the ASUS motherboard used in our article, you can also change the fan speed depending on the temperature parameters. In addition, you can set the CPU alarm temperature, which will be activated when overheating. Another possibility is to turn off the computer after exceeding the threshold temperature. Then your processor will not burn out from overheating or in any extreme situations.
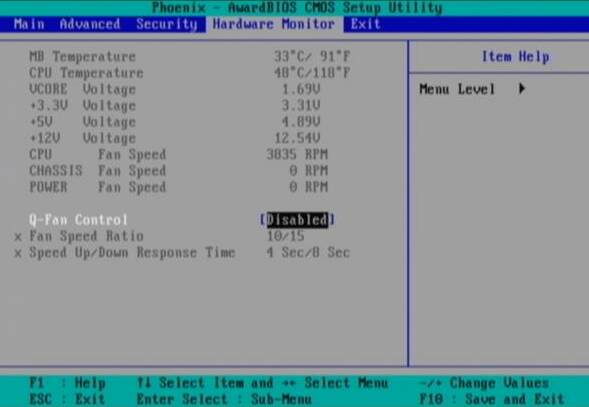
If the BIOS has such features, then all of them are listed in the section and clearly signed. Since modern processors are very hot, we recommend that you enable monitoring functions to prevent potential dangers.
Each CPU has its own temperature limits. For example, for AMD Athlon they are listed at the beginning of this article. In general, if the BIOS has the option to issue a warning beep or shut down the computer if a specific temperature is reached or exceeded, then they usually indicate several temperature values \u200b\u200bfrom which you can select any. We recommend setting the second temperature after the hottest.
BIOS Setup Summary
Since the BIOS of modern computers varies greatly, the BIOS of your computer may have some features not covered in this article. For getting additional information and for answers to questions, we recommend that you refer to the following websites: Wim's BIOS and Adrian's RojakPot .
Good luck with tuning and optimizing the BIOS!